2021-12-13 13:44 작성
My SQL basic 메모
Table of contents
EXISTS 도입
EXISTS 연산자는 true 혹은 false를 반환하는 Boolean 연산자다. EXISTS 연산자는 종종 subquery에 의해 반환되는 rows의 존재 여부를 테스트하기 위해 사용된다.
다음은 EXISTS 연산자의 기본 문법이다:
SELECT
select_list
FROM
a_table
WHERE
[NOT] EXISTS(subquery);
만약 subquery가 적어도 하나의 row를 반환하면, EXISTS 연산자는 true를 반환하고 그렇지 않으면 false를 반환한다.
추가로, EXISTS 연산자는 매칭되는 row를 발견하자마자 그 즉시 그 다음의 처리를 종료하기 때문에 쿼리의 성능을 개선하는데 도움을 줄 수 있다.
NOT 연산자는 EXISTS 연산자를 무효화한다. 달리 말하자면, NOT EXISTS는 만약 subquery가 어떤 row도 반환하지 않으면 true를 반환하고 그렇지 않을 경우 false를 반환한다.
EXISTS 연산자 예시
SELECT EXISTS 예시
다음의 customers와 orders tables를 살펴보자.
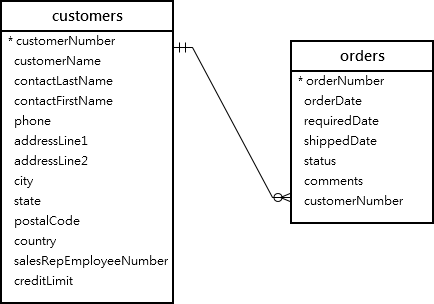
다음의 구문은 적어도 1개의 order를 가지고 있는 customer를 찾는데 EXISTS 연산자를 사용한다.
SELECT
customerNumber,
customerName
FROM
customers
WHERE
EXISTS(
SELECT
1
FROM
orders
WHERE
orders.customernumber
= customers.customernumber
);
output:
| customerNumber | customerName |
|---|---|
| 103 | Atelier graphique |
| 112 | Signal Gift Stores |
| 114 | Australian Collectors, Co. |
| 119 | La Rochelle Gifts |
| 121 | Baane Mini Imports |
| 124 | Mini Gifts Distributors Ltd. |
| 128 | Blauer See Auto, Co. |
| 129 | Mini Wheels Co. |
위 예시에서 쿼리는 customers table의 각각의 row에 대해 orders table의 customerNumber를 확인한다. 만약 customers table에서 나타나는 customerNumber가 orders table에서 존재하면 subquery는 매칭되는 첫번째 row를 반환한다. 그 결과 EXISTS 연산자는 true를 반환하고 orders table을 조사하는 것을 멈춘다. 그렇지 않은 경우 subquery는 어떤 row도 반환하지 않고 false를 반환한다.
다음의 예시는 어떤 orders도 가지고 있지 않은 customer를 찾는데 NOT EXISTS 연사자를 사용한다.
SELECT
customerNumber,
customerName
FROM
customers
WHERE
NOT EXISTS(
SELECT
1
FROM
orders
WHERE
orders.customernumber = customers.customernumber
);
output:
| customerNumber | customerName |
|---|---|
| 125 | Havel & Zbyszek Co |
| 168 | American Souvenirs Inc |
| 169 | Porto Imports Co. |
| 206 | Asian Shopping Network, Co |
| 223 | Natürlich Autos |
| 237 | ANG Resellers |
UPDATE EXISTS 예시
San Francisco에 있는 오피스에서 일하는 employees의 내선번호를 업데이트해야 한다고 가정해보자.
다음의 구문은 San Francisco의 오피스에서 일하는 employees를 찾는 구문이다:
SELECT
employeenumber,
firstname,
lastname,
extension
FROM
employees
WHERE
EXISTS(
SELECT
1
FROM
offices
WHERE
city = 'San Francisco' AND
offices.officeCode = employees.officeCode
);
output:
| employeenumber | firstname | lastname | extension |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1002 | Diane | Murphy | x5800 |
| 1056 | Mary | Patterson | x4611 |
| 1076 | Jeff | Firrelli | x9273 |
| 1143 | Anthony | Bow | x5428 |
| 1165 | Leslie | Jennings | x3291 |
| 1166 | Leslie | Thompson | x4065 |
다음의 예시에서는 San Francisco의 오피스에서 일하는 employees의 내선번호에 1을 더한다.
UPDATE employees
SET
extension = CONCAT(extension, '1')
WHERE
EXISTS(
SELECT
1
FROM
offices
WHERE
city = 'San Francisco'
AND offices.officeCode = employees.officeCode
);
- 첫째,
WHERE구문의EXISTS연산자는 San Francisco의 오피스에서 일하는 employees만을 찾는다. - 둘째,
CONCAT()function은 내선번호에 1을 더한다.
쿼리가 성공한 뒤 다시 값을 조회하면 다음과 같은 결과값을 얻을 수 있다.
| employeenumber | firstname | lastname | extension |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1002 | Diane | Murphy | x58001 |
| 1056 | Mary | Patterson | x46111 |
| 1076 | Jeff | Firrelli | x92731 |
| 1143 | Anthony | Bow | x54281 |
| 1165 | Leslie | Jennings | x32911 |
| 1166 | Leslie | Thompson | x40651 |
INSERT EXISTS 예시
별개의 table에 sales order가 없는 customers의 정보를 보관하기를 원한다고 가정하자. 이것을 위해 다음과 같은 단계를 거쳐야 한다:
첫째, customers table에서 구조(structure)를 복사해 customers를 보관할 새로운 table을 생성해야 한다.
CREATE TABLE customers_archive
LIKE customers;
둘째, 다음의 INSERT 구문을 사용해 customers_archive table에 어떤 sales order도 존재하지 않는 customers를 집어 넣는다.
INSERT INTO customers_archive
SELECT *
FROM customers
WHERE NOT EXISTS(
SELECT 1
FROM
orders
WHERE
orders.customernumber = customers.customernumber
);
SELECT * FROM customers_archive;
output:
| customerNumber | customerName | contactLastName | contactFirstName | phone | addressLine1 | addressLine2 | city | state | postalCode | country | salesRepEmployeeNumber | creditLimit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 125 | Havel & Zbyszek Co | Piestrzeniewicz | Zbyszek | (26) 642-7555 | ul. Filtrowa 68 | NULL | Warszawa | NULL | 01-012 | Poland | NULL | 0.00 |
| 168 | American Souvenirs Inc | Franco | Keith | 2035557845 | 149 Spinnaker Dr. | Suite 101 | New Haven | CT | 97823 | USA | 1286 | 0.00 |
| 169 | Porto Imports Co. | de Castro | Isabel | (1) 356-5555 | Estrada da saúde n. 58 | NULL | Lisboa | NULL | 1756 | Portugal | NULL | 0.00 |
| 206 | Asian Shopping Network, Co | Walker | Brydey | +612 9411 1555 | Suntec Tower Three | 8 Temasek | Singapore | NULL | 038988 | Singapore | NULL | 0.00 |
| 223 | Natürlich Autos | Kloss | Horst | 0372-555188 | Taucherstraße 10 | NULL | Cunewalde | NULL | 01307 | Germany | NULL | 0.00 |
| 237 | ANG Resellers | Camino | Alejandra | (91) 745 6555 | Gran Vía, 1 | NULL | Madrid | NULL | 28001 | Spain | NULL | 0.00 |
…
DELETE EXISTS 예시
customer 데이터를 보관하는데 있어 마지막 과업은 customers table에서 customers_archive table에 존재하는 customers를 삭제하는 것이다.
이를 위해 DELETE 구문에서 WHERE 절 안에 EXISTS 연산자를 사용한다:
DELETE FROM customers
WHERE EXISTS(
SELECT
1
FROM
customers_archive a
WHERE
a.customernumber = customers.customernumber
);
EXISTS 연산자 vs. IN 연산자
적어도 하나의 order가 있는 customer를 찾기 위해 IN 연산자를 사용할 수 있다:
SELECT
customerNumber,
customerName
FROM
customers
WHERE
customerNumber IN (
SELECT
customerNumber
FROM
orders
);
output:
| customerNumber | customerName |
|---|---|
| 103 | Atelier graphique |
| 112 | Signal Gift Stores |
| 114 | Australian Collectors, Co. |
| 119 | La Rochelle Gifts |
| 121 | Baane Mini Imports |
| 124 | Mini Gifts Distributors Ltd. |
| 128 | Blauer See Auto, Co. |
| 129 | Mini Wheels Co. |
| 131 | Land of Toys Inc. |
EXPLAIN 구문을 이용해 EXISTS와 IN을 각각 사용하는 쿼리를 비교해보자.
EXPLAIN SELECT
customerNumber,
customerName
FROM
customers
WHERE
EXISTS(
SELECT
1
FROM
orders
WHERE
orders.customernumber = customers.customernumber
);
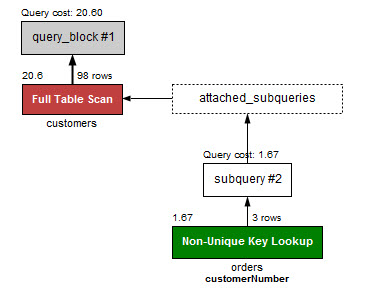
이제 IN 연산자를 사용한 쿼리의 퍼포먼스를 확인하자.
EXPLAIN SELECT
customerNumber, customerName
FROM
customers
WHERE
customerNumber IN (SELECT
customerNumber
FROM
orders);
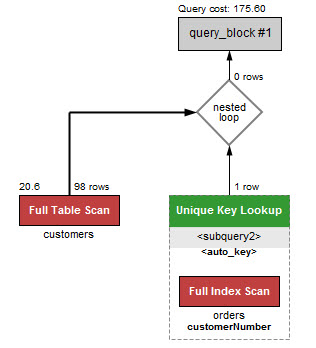
EXISTS 연산자를 사용하는 쿼리가 IN 연산자를 사용하는 쿼리보다 훨씬 빠르다.
그 이유는 EXISTS 연산자는 “at least found” 원칙에 기반하기 때문이다. EXISTS는 매칭되는 row가 발견되면 스캐닝을 멈춘다.
반면에 IN 연산자는 subquery와 통합되어 있을 때 subquery를 먼저 실행하고 그 결과를 바탕으로 전체 쿼리를 실행한다.
일반적으로 추천되는 방법은 만약 subquery가 큰 데이터의 용량을 포함할 경우 EXISTS가 더 낫고, 반면에 subquery가 작은 데이터 용량을 가질 경우 IN 연산자가 더 빠른 퍼포먼스를 제공한다.
예를 들어, 다음의 구문은 IN 연산자를 사용하여 San Francisco의 오피스에서 일하는 모든 employees를 선택한다.
SELECT
employeenumber,
firstname,
lastname
FROM
employees
WHERE
officeCode IN (SELECT
officeCode
FROM
offices
WHERE
offices.city = 'San Francisco'
);
쿼리의 퍼포먼스를 확인해보자.
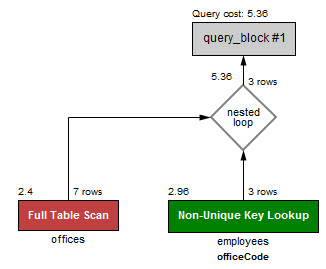
첫 예시에서 사용했던 EXISTS 연산자보다 근소하게 더 빠르다. EXSITS 연산자를 사용했을 때의 퍼포먼스는 다음과 같다:
SELECT
customerNumber,
customerName
FROM
customers
WHERE
EXISTS(
SELECT
1
FROM
orders
WHERE
orders.customernumber = customers.customernumber);
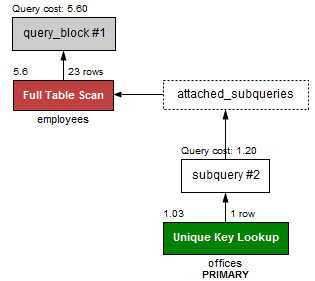
EXISTS의 예시에서는 각각의 customers의 모든 데이터를 가져와 비교하며 IN 예시에서는 officeCode만 가져와 비교한다.